What is Solderability Test?
Welding is the process of combining or joining metals or thermoplastics by melting and adding a filler material to the welded area to form a strong joint. Weldability is used to define whether two materials can be welded together without any cracks or not. Therefore, a weldable material is a material that can be welded easily without any risks of cracks.
The solderability test refers to the qualitative and quantitative evaluation of the solderability of components, PCB boards, PADs, solders and fluxes by the wetting balance method.
The modern electronic industry depends upon high-quality interconnection technology and high-quality, zero-defect welding processes. IC packaging, electronic components assembly and circuit boards require welding; therefore, solderability testing is essential.
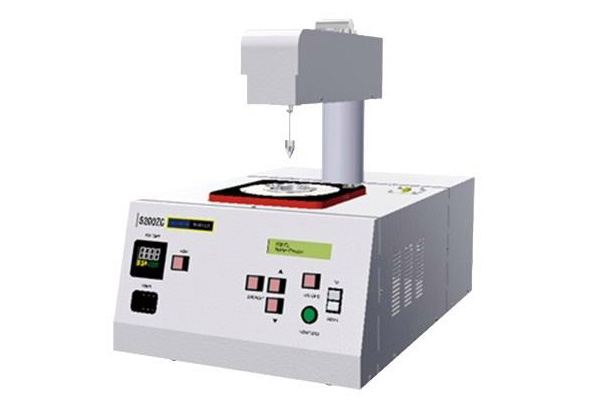
The principle of testing includes sensing the force through the sensor and combining time to evaluate the strength of tin climbing and the speed of wetting. The sample is positioned on the fixture and connected to the sensor in a stable manner. Then, the sample is immersed in the solder paste at the set temperature. At this point, the force and time are sent to the PC through the sensor, which forms the curve and data.
Solderability Test Methods
The edge dip soldering test, floating soldering test, wave soldering test, wetting balancing method test, and other methods have been suggested by major international standard organizations such as IEC, IPC, DIN, and JIS.
What is a Solderability Tester?
A solderability tester is an automated instrument employed to perform quantitative solderability tests on the welded ends of electronic components. It offers quick, accurate and objective test results.
Application:
- In cases like step temperature rise and rapid temperature rise in a short duration, the wettability of the flux and solder of the chip component is evaluated.
- The solder ball method is employed to analyze the soldering performance of chip components and printed circuit board vias.
- The wettability of the flux and solder for electronic components are evaluated in a nitrogen atmosphere.
- Wetting time, wetting stress, surface tension and detentacle can be determined when connected to a computer.
Precautions before using the solderability tester:
The temperature of a solderability tester can exceed 300 ℃. Therefore; it is strictly advised not to touch anything with bare hands to avoid high-degree burns. Additionally, any substance that contains water must not be put into the solder pot where the solder has melted, or else the solder will explode, which may be fatal.
The temperature of the solderability tester can be as high as 300 ℃ after the solder is melted. It is strictly forbidden to touch it with bare hands to avoid burns. Drying in Wuxi should be avoided.
Methods of Solderability Testing in Electronic Inspection:
Several methods are present for electronic testing. As described previously, the solderability test is the qualitative and quantitative evaluation of the solderability of components and other things.. Therefore, the solderability test primarily includes the balance method, which is ideal for parts with thinner pins, whereas the tin furnace method is suitable for all electronic components.
Balance method:
What are the requirements for the test equipment used for tin balancing?
- Tin bath or solder ball with precise temperature control.
- Precision control system and a mechanism capable of moving the tin bath/solder ball up and down.
- Precision balance or micro-force testing device.
- A test result recorder.
- Any related hardware and analysis software.
Wetting balance is another name for a wetting ability testing machine. The basic principle is the generation of action flow at the moment of contact between a rising tin bath and the part to be tested. Wetting Balance is the process of changing until the force reaches equilibrium and quits.
Tin furnace method:
- Purpose:
Solderability evaluation methods for DIP, through-hole axial, and SMD devices are used to determine their ability to solder to other Pb-containing or Pb-free surfaces according to JESD22-B102D (reference standard)
2. Inspection and failure criteria:
All parts under 10x to 20x magnification must be inspected. A minimum of 95% solder coverage must be present in each lead. The total number of pinholes, voids, porosity, non-wetting or de-wetting shall not exceed 5% of the inspection area, and each device’s pins must not be bridged.
What are the solderability testing methods for SMT components?
SMT component solderability testing is primarily concerned with the solderability of solder terminals or pins. Solderability problems arise from oxidation or contamination on the component solder terminal surfaces or pins. It’s also the main factor affecting the reliability of SMA soldering. Therefore, to ensure the reliability of soldering, packing conditions and environmental conditions must be looked upon closely, and necessary measures to eliminate the risk of components being exposed for a long time before soldering must be taken. Component solderability can be tested in a variety of ways. Some of the most regularly utilized test methods are listed below.
Solderability testing method of SMT components:
Welding bath method:
The solder bath moisturizing method is the most accurate component solderability test method. The test is based on visual inspection. The test process includes immersing the sample in flux and removing it. Later, the remaining flux is submerged in the molten solder bath for double the time of production soldering time. Take it out and observe visually.
The test is done with the help of an immersion tester who regulates the sample’s immersion depth and residence time as per the parameters. This way, the results are rapid and accurate; however, the visual observation only gives a qualitative conclusion. Hence, not preferred for situations where quantitative accuracy is the point of focus. The fast and intuitive test requirements of SMT assembly production sites are well-suited for this test. All samples to be tested must have continuous solder covering, or at least each sample must be qualified with a solder coverage of more than 95 per cent, according to the qualification standards.
Solder ball method:
The solder ball method is relatively simple and more focused on the qualitative aspect. Horizontally place the components and submerge them directly into the solder balls at regular speed. Observe and record the time it takes for the lead to be wet and covered by solder balls. Determine the solderability by the length of the recorded time. The qualification criteria for the solderability test by solder ball method are:
- Time taken by the lead to be wet by the solder ball is approximately 1S; if it exceeds 2s, it’s not regarded as qualified.
Wet weighing:
The process’s basic principle involves suspending the component’s sample on the active scale’s weighing rod. Summer the sample in a constant temperature of molten solder until the regular depth. Now, the sensor measures the resultant force in the vertical direction of the buoyancy force and surface tension on the immersed sample and converts it into a single. A high-speed characteristic curve recorder records it as a force-time function curve. The results are achieved by comparing the curve with an ideal wet weight curve.
The moisture balance tester is used in the moisture weighing method. Once the sample is submerged in the molten solder at a pre-determined depth, the liquid level of the solder is initially pressed down into a meniscus shape. This is primarily because the cohesion of the solder exceeds the adhesion between the molten solder and the test sample.. Once the sample archives the soldering temperature, the adhesion between the sample and molten solder becomes greater than the cohesive forces. The molten solder wets the sample, making the meniscus bend up until 6 equals 90°. Wetting continues until the upper meniscus is 9 less than 90°. A downward pull effect occurs until the vertical weight of the surface tension and buoyancy are equal.
PCB Solderability Test:
The welding quality is bound to affect the quality of the entire machine during the production of printed circuit boards. Common problems are poor wetting, false soldering, virtual soldering, poor tinning etc. These problems may be due to the following reasons:
- The quality of raw materials does not meet the requirements, which results in poor quality and performance.
- The temperature, degree of wetting and length of time affect the formation of the intermetallic compound structure.
- The quality of the components and the PCB board must be up to standard. Furthermore, environmental factors and other related parameters can significantly affect the quality of components.
- The product’s wetting performance is influenced by its surface coating. Variable coating types have different solderability, and substantial coating ageing will make the product’s solderability poorer.
How can the root cause of inaccuracy be determined?
It’s a well-established fact that solderability test is primarily for qualitative and quantitative assessment of related components. Any problem associated with soldering can be detected with the help of testing. Solderability testing has been helping industries evaluate quality standards. Lead-free technology has taken over the world, and updated requirements regarding it have been put forward. Solderability testing has become necessary in every aspect related to soldering. To ensure the quality of soldering, we need to conduct scientific solderability tests on printed circuit boards.




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.